
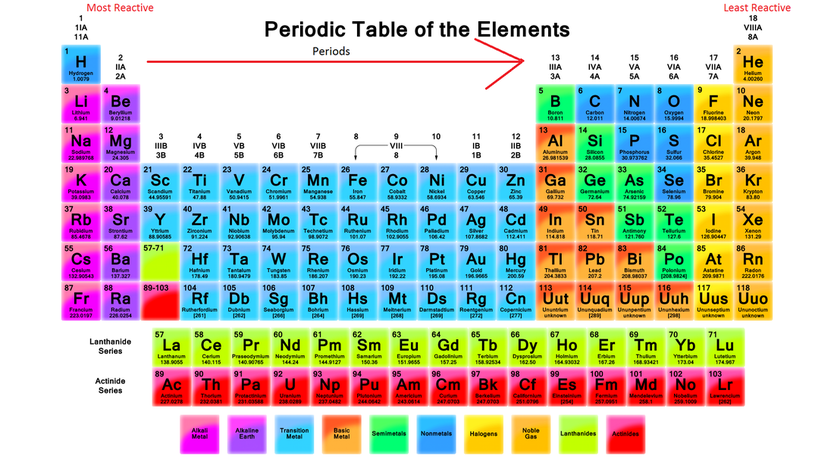
This provides the driving force for metal displacement reaction. Out of the elements in the reactivity series, the most reactive metal is potassium and the least reactive.
#REACTIVITY TABLE OF ELEMENTS FREE#
In other words, a highly reactive metal prefers to be a cation while its less reactive friend prefers to be a free element. Different metals have different reactivities. A less reactive metal is a hoarder - it would rather have its valence electrons.
#REACTIVITY TABLE OF ELEMENTS SERIES#
The reactivity series tells us how much a metal wants to be a cationĪ more reactive metal donates electrons more readily to form a cation. More reactive metals react more vigorously, increasing the rate of effervescence of hydrogen gas.Ĥ. Secondly, reactivity affects the rate of reaction. The unreactive metals do not react at all, even when we use strong acid or high temperature.Moderately reactive metals require a higher temperature to react with water.Highly reactive metals are trigger happy, reacting with acids and even water at room temperature.Reactive metal + hydrochloric acid ⟶ metal chloride + hydrogenįirstly, reactivity affects what a metal can react with. Reactive metal + steam ⟶ metal oxide + hydrogen Reactive metal + water ⟶ metal hydroxide + hydrogen The reactivity series tells us if a reaction will happen and under what conditions Metal The trio sit in the same column within the transition metal hood.ģ.
The Trio of Unreactive MetalsĪnd the least reactive metals we need to know are copper, silver, and gold. Lead in Group IV is also moderately reactive. Transition metals are generally less reactive than the main group metals. Within each group, the metal lower down the group is more reactive. The data provided by the reactivity series can be used to predict whether a metal can displace another in a single displacement reaction. They have the greatest tendency to lose electrons to form cations.įor the four metals we need to know, those from Group I are more reactive than those from Group II. The reactivity series of metals, also known as the activity series, refers to the arrangement of metals in the descending order of their reactivities. Group I alkali metals and Group II alkaline earth metals are the most reactive. R adium is extremely radioactive, and only occurs as part of the decay chains of heavier elements such as thorium and uranium.The reactivity series is written into the Periodic Table! Highly Reactive Group I and II Metals Saturated Unsaturated and Supersaturated.Reaction Quotient and Le Chatelier's Principle.Hussain, Dept of Natural Sciences (Chemistry) LaGuardia Community College Goals: In this experiment you will verify the similarity of family properties by carrying out a number of chemical reactions on representative elements (actually using ions of the elements) and using. In chemical compound: The periodic table be grouped according to their chemical reactivity. Prediction of Element Properties Based on Periodic Trends The Periodic Table : Reactivity of Elements Prepared by Prof.Molecular Structures of Acids and Bases.Ion and Atom Photoelectron Spectroscopy.Elemental Composition of Pure Substances.More reactive elements tend to gain or lose electrons. Application of Le Chatelier's Principle Reactivity is an elements ability to ionize (gain or lose electrons) or share electrons.Structure, Composition & Properties of Metals and Alloys.Intramolecular Force and Potential Energy.Variable Oxidation State of Transition Elements.Transition Metal Ions in Aqueous Solution.Single and Double Replacement Reactions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
